Executive Summary
Many of our academic clients who come on board already have an annuity product offered by Teachers Insurance and Annuity Association of America (TIAA) called the TIAA Traditional. While this can be a good fit for their retirement savings, we also find many do not fully understand the TIAA Traditional Account. In large part, this is because it differs from many other types of investment vehicles. Unlike a mutual fund, which acts more like a basket of investments, many products through TIAA are Annuity Products. Annuity products vary greatly across the financial world, and while they have an investment component to them, annuities are also an insurance product. To help demystify the TIAA Traditional, I’ll start with a brief education on annuity-related terminology, then highlight some key aspects of TIAA Traditional, and finish off with some key considerations. The intent here is to provide education on an annuity product and should not be considered investment advice nor a recommendation to execute or abstain from action.
Annuities – An Overview
Naturally, let us start off with some Shakespeare. In his 16th Century play, Julius Caesar, a Roman conspirator and assassin to Caesar, Casca, chats with Cassius about a speech given by Cicero, saying “But those that understood him smiled at one another and shook their heads. But for mine own part, it was Greek to me.” Casca spoke Latin, but I’m guessing annuity terminology may as well be Greek to us all. Aye, let us sheathe our daggers, I’ll explain below:
⠀⠀⠀1) Immediate Annuity Contracts provide a stream of guaranteed income payments (the Income Phase) to an annuitant immediately following a one-time contribution. Conversely, Deferred Annuity Contracts can have a one-time contribution or a series of contributions, where the contract value may grow over time (the Accumulation Phase) before annuitizing later to begin the Income Phase.
⠀⠀⠀2) Fixed Annuity Contracts guarantee a minimum interest credit on the contract value during the Accumulation Phase and pay out a fixed income stream during the Income Phase, in part, based upon interest rate guarantees at the time of purchase.
⠀⠀⠀3) Variable Annuity Contracts allow for contributions to be allocated to sub-accounts which can be invested in stocks, bonds, and other investments; these sub-accounts’ values may vary depending on the performance of underlying investments. As such, the annuitant bears investment risk during the Accumulation Phase. During the Income Phase, payments can either be fixed or they can also vary depending on underlying performance.
⠀⠀⠀4) Index Annuity Contracts have both fixed and variable features, with interest credits tied to external investment indices but with a minimum guaranteed rate.
⠀⠀⠀5) Annuitant An individual who currently has an annuity contract with an insurance company; they can be in either the Accumulation or Income Phase.
At their core, annuities are financial contracts between an individual (also known as the “annuitant” or “insured”) and the insurance company. You (“the annuitant”) offers money in the form of contributions or premiums in exchange for certain guarantees made by the insurance company. The most common guarantees are for income. See below for more about the guarantees.
Phew! With that out of the way, the Ides of March have been held at bay. Now, let us highlight some key features of the TIAA Traditional.
Availability
TIAA Traditional is a deferred fixed-annuity, meaning that it has minimum guaranteed interest rates, an Accumulation Phase, and if an annuitant decides to do so—an Income Phase.
It is available to those who have an employer-sponsored retirement plan with TIAA (e.g., mandatory 401(a) plans or optional 403(b) plans) that offers TIAA Traditional as an investment option. TIAA Traditional is also available within TIAA IRAs to eligible individuals.
It should be noted that even when TIAA Traditional is an option within a retirement plan, interest rates, contractual guarantees, and other terms and conditions depend on the TIAA Traditional contract-type, which vary from plan-to-plan. (remember “contract-type,” it will come up later).
Guaranteed Interest Rates
We find the most attractive feature our clients like about the TIAA Traditional is the interest paid under this account. The interest is made up of two components:
⠀⠀⠀1) A guaranteed minimum interest rate
⠀⠀⠀2) An additional amount above the guaranteed minimum, as declared periodically by TIAA.
The combination of these two is known as the effective interest rate, or current rate. A full listing of current and historic effective rates and minimum rates can be found HERE². For example, as of this drafting, the TIAA Traditional under the Group Supplemental Retirement Annuity (GSRA) which we commonly see through the University of Illinois 403b is paying:
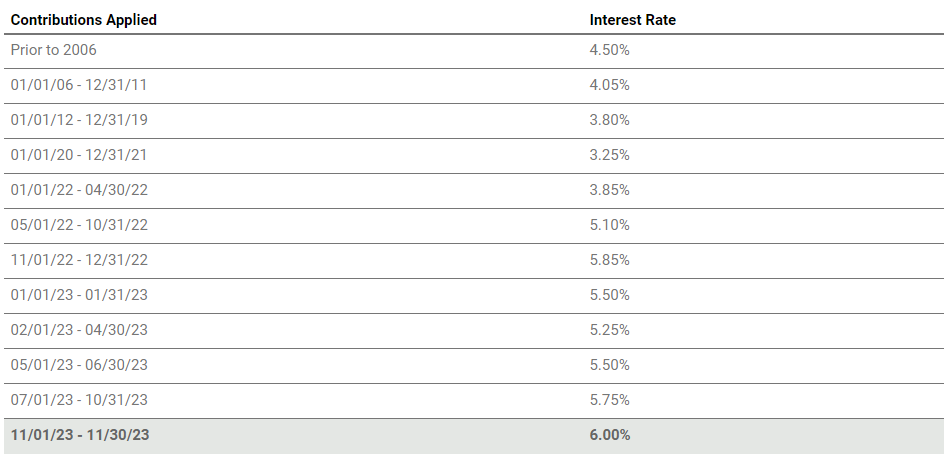
The timing of a contribution also affects interest credits. TIAA Traditional credits interest based on the time period during which you make the contribution or transfers balances in. Different time periods can have different minimum, effective, and income payout rates. Here is the chart of this history of the TIAA Traditional under the Group Supplemental Retirement Annuity (GSRA)³:
Risks
As with all investment products, there are risks to consider. As the TIAA Traditional is an insurance product, the guaranteed returns are backed by TIAA. When you invest into this account, TIAA is pooling the funds from all participants and investing the money to generate the income necessary to make interest payments and satisfy the income requirements of the participants who have annuitized. While you as the participants may not directly see the ups and downs of investing you might see through a mutual fund, all funds are subject to the claims-paying ability of TIAA⁴
To evaluate the risk of this investment, you need to consider the financial strength of TIAA. There are firms out there that do provide some evaluation, such as Fitch Ratings. In their August 22, 2023, rating action commentary⁵ they expressed, “Fitch Ratings has affirmed Teachers Insurance and Annuity Association of America's (TIAA) 'AAA' Insurer Financial Strength (IFS) ratings, the 'AA+' Long-Term Issuer Default Rating (IDR) and the 'AA' surplus notes rating as well as the ratings of its wholly owned insurance subsidiaries and affiliates. The Rating Outlook for TIAA and subsidiaries is Stable.” It’s important to note these ratings are not perfect and have been wrong in the past. You should review such ratings, discuss them with qualified professionals, draw informed conclusions on an insurance company’s ratings and ratings outlook, and reflect on potential impacts and risks they present to a potential annuitant.
One way to mitigate this risk would be to consider limiting your investment into the TIAA Traditional to mitigate this risk. In the event of illiquidity of TIAA, such as bankruptcy, there may be additional backing through the Life & Health Insurance Guaranty Association. For example, in the State of Illinois, annuity products are protected from losses by the insurer by up to $250,000. You can find the full list of states and insurance amounts on their website by following this link.
Liquidity
Unlike other stock or bond based mutual funds you might commonly invest in through a Retirement Plan, the annuity structure of TIAA Traditional can also be a downside. As an annuity is ultimately designed to provide a lifetime stream of income at retirement, some plans may restrict withdrawals from the TIAA Traditional account. Withdrawals can apply to both your ability to take a distribution from the account as well as your ability to transfer between investment choices within your plan.
For my astute readers out there, I am going to ask you to recall a term mentioned earlier—contract-type. The contract-types with the highest minimum and effective rates are the most restrictive with respect to withdrawals. In other words, there is no such thing as a free lunch. Higher interest payments are gained by locking up your money.
TIAA puts contract-types into two categories: Delayed Liquidity and Full Liquidity. Below you will find a table directly from TIAA outlining the contract-types and their corresponding TIAA Traditional withdrawal rules.
Figure 1: https://www.tiaa.org/public/retire/financial-products/annuities/retirement-plan-annuities/tiaa-traditional-annuity/contract-rules, Accessed 10/31/23⁶
With delayed liquidity contracts, an annuitant is still able to move funds out of TIAA Traditional into other available investment options within the same retirement plan, but it would need to happen over a series of years.
Furthermore, if an employee can withdraw funds from their employer-sponsored plan, the same logic follows. Funds can be withdrawn out of TIAA Traditional and, if desired, out of the TIAA retirement plan altogether, though again it would occur over a series of years via what’s known as a Transfer Payout Annuity (TPA). These withdrawn funds can be rolled over tax-free to a new employer plan, transferred tax-free to an IRA, or taken as distribution (subject to income tax).
In both cases, the annuitant has received the benefit of guaranteed interest accruals during accumulation, then forfeited future guaranteed interest accruals and the option of a deferred income stream in exchange for the added flexibility that alternative investments and investment vehicles may provide.
Fees
To quote TIAA⁷
“TIAA Traditional is not an investment product for purposes of federal securities laws. It is a guaranteed insurance contract. Therefore, unlike a variable annuity or mutual fund, TIAA Traditional does not include an identifiable ‘expense ratio’ or ‘fee’ like you might see published for a mutual fund or variable annuity.”
“How is TIAA compensated if there isn’t an expense ratio? TIAA’s compensation is the difference between the interest TIAA earns on supporting assets and the interest TIAA credits on TIAA Traditional accumulations. That difference covers expenses and contributes to the financial strength of TIAA.”
Putting It All Together
Because of the guaranteed minimum interest rates and potential for additional interest credits, it is in our opinion that balances TIAA Traditional could be viewed as part of an overall investment strategy. Though, it differs from other fixed interest rate investment vehicles (like a Certificate of Deposit, for example) in key areas including, but not limited to, default risk, liquidity risk, and interest rate risk. These key differences and suitable alternatives should be reviewed and understood fully.
For someone who understands these risks and potential alternatives and chooses to view TIAA Traditional as part of an overall investment strategy, they could utilize the annuity product as a means of accumulating interest until a later point in time. Then, depending on their unique circumstances, they could leave balances in place, annuitize the balances, or roll funds over tax-free to other investments vehicles (depending on delayed/full liquidity contract-types).
Overall, we see the TIAA Traditional as a potentially viable part of someone’s investment and retirement plan, though it always depends on someone’s unique goals, circumstances, tolerance, capacity for risk, and understanding of this type of financial product.
In Summary
The TIAA Traditional fixed-annuity contract may have a place within a well-constructed investment portfolio and/or retirement cashflow plan. It has guaranteed minimum interest rates, discretionary additional interest credits, and optionality for guaranteed income streams. On the other hand, its withdrawal/transfer restrictions and guarantees backed by claims-paying ability should be carefully considered as part of the decision-making process for including this as part of one’s retirement and/or investment plan.
Navigating withdrawal restrictions, assessing annuitization and its alternatives, and deciding if TIAA Traditional is suitable for an individual’s investment portfolio and cashflow plan are discussions and decisions that a qualified financial planner can help with.
Our team of financial advisors has years of experience working with faculty and administrators both in the IL State Universities Retirement System (SURS) and beyond the Prairie State’s borders. We can help you create a comprehensive investment, retirement, and tax plan that suits your unique needs, goals, and aspirations. Please visit our “Resources” site page for more information.
Footnotes:
[2] https://www.tiaa.org/public/investment-performance?defaultview=faonly (Accessed: 10/31/23)
[3]https://www.tiaa.org/public/investment-performance/investment/profile?ticker=47933633 (Accessed: 11/7/2023)
[4] https://www.tiaa.org/public/pdf/How_TIAA_Supports_Guarantees.pdf (Accessed 11/6/23)
[5]https://www.fitchratings.com/research/insurance/fitch-affirms-tiaa-ratings-outlook-stable-22-08-2023 (Accessed: 11/6/23)
[6] https://www.tiaa.org/public/retire/financial-products/annuities/retirement-plan-annuities/tiaa-traditional-annuity/contract-rules, Accessed 10/31/23